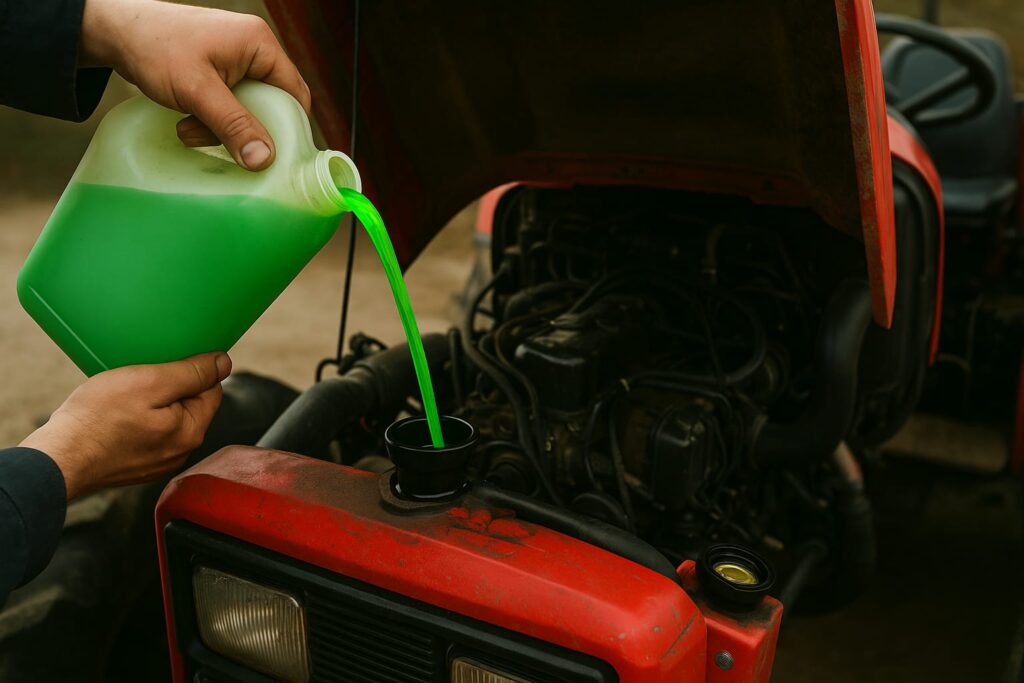
It is very important for a farmer or a professional tractor operator to know when and how to service their tractor.
Because timely servicing of the tractor is very important; it keeps the engine healthy and working efficiently.
When it comes to servicing, the most important parameter is the type of engine oil being used. The company specifies what type of engine oil to use and also provides guidelines on when to change it. According to the company, the engine oil should be changed every 2:30 to 300 hours of operation.
Now, the most important thing is that farmers need to know that If you are getting your tractor serviced at an external service center. Then how to get their tractors serviced professionally, and what kind of tools and engine oils and other service materials they should use. This is extremely important.
What things should you keep in mind when getting your tractor serviced. (Outside service center) ?- Selection of service center.
- selection of engine oil.
- selection of service kit.
- Inspect the fuel line.
- Inspect the radiator and water supply line.
- Check the air intake capacity and its lines.
- Clutch and Break adjustment.
- Comprehensive health checkup.
- Selection of service center. If you are going to get your tractor serviced, you should ensure that you take it to an authorized service center of the brand of tractor you own. Authorized service centers have professional mechanics who will thoroughly inspect your tractor and fix any problems it may have. The service center has all kinds of mechanical tools and original spare parts for your tractor. If your vehicle has any kind of parts problem, they will replace it so that you face minimal inconvenience. Now, if you are getting the service done from an outside service provider, make sure you are completely satisfied that the mechanic you are using is knowledgeable and skilled.
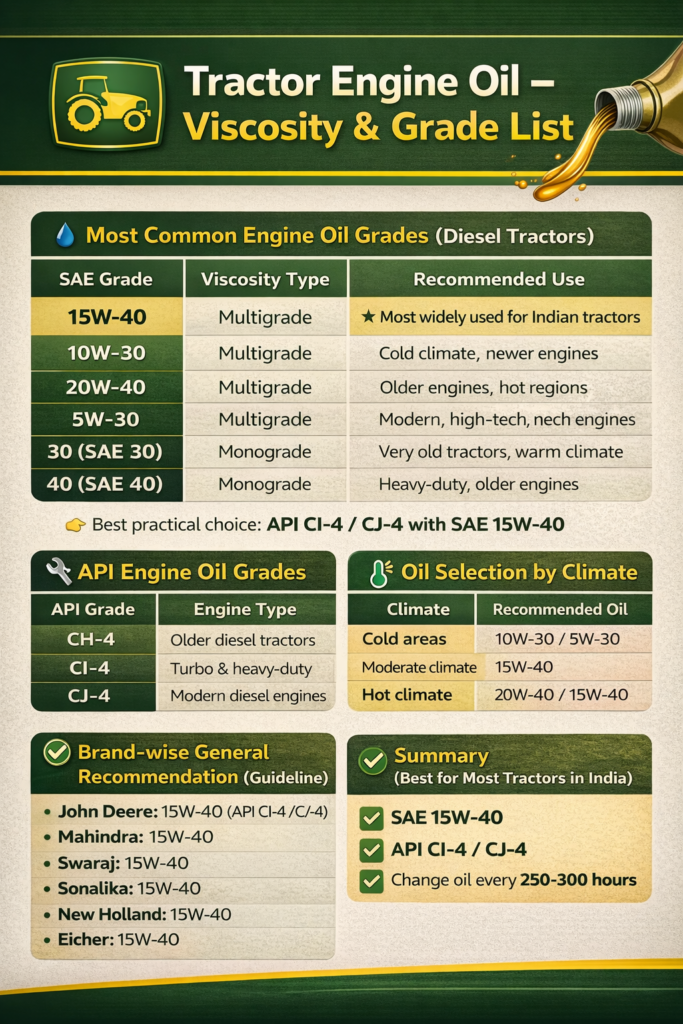
- Selection of engine oil. Many types of engine oils are available in the market for tractors and commercial vehicles. It’s your responsibility to determine which one is best for you, as some engine oils are cheaper while others are more expensive. Cheaper engine oils are suitable for shorter operating hours, while expensive ones last much longer. Naturally, the expensive engine oils are generally available in much better quality. And better engine oils provide better protection to the engine. Two main types of engine oil are used in tractors: 20W-40 and 15W-40. Currently, three grades are commonly available: CF, CH, and CI. These are available in both 20W40 and 15W40 viscosities. If we talk about the best grade, the superior grade (CI+), whether it’s 15W40 or 20W40, provides engine protection for at least 800 to 1000 hours. In contrast, the CF grade provides protection for 2:30 to 3 hours, and the CH grade provides protection for approximately 4 hours.
- some branded lubricant compny famous in india. Castrol India, / Indian Oil (Servo), / Gulf Oil Lubricants India Ltd. HPCL (HP Lubricants) & BPCL (MAK): Valvoline: Veedol: Savita Oil Technologies (Savsol):
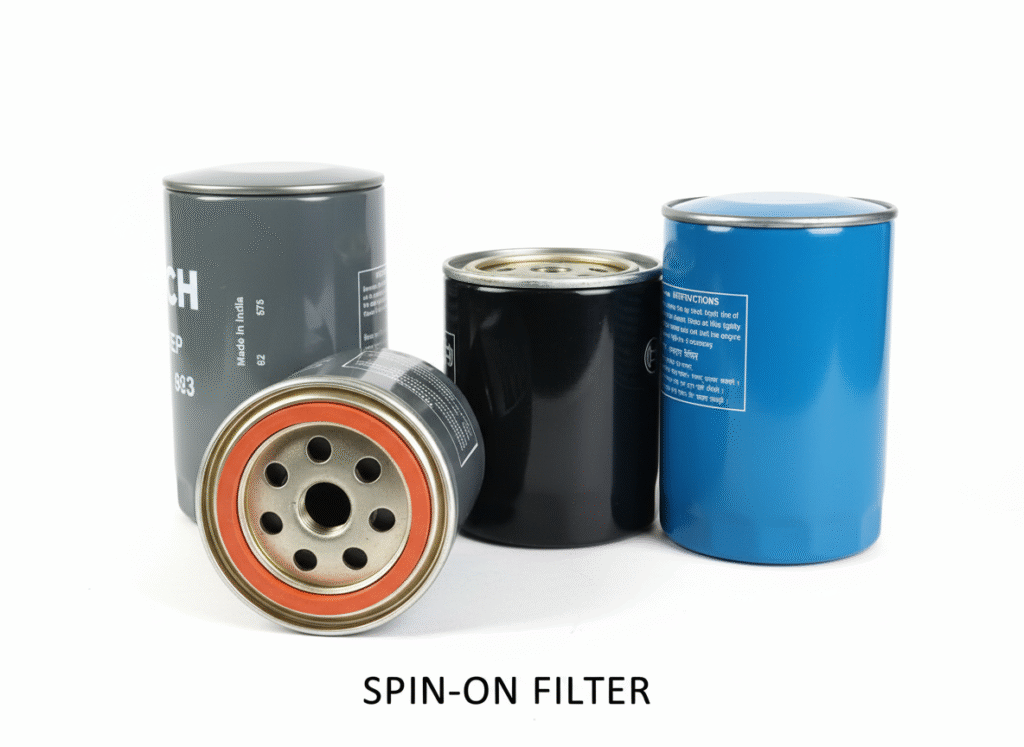
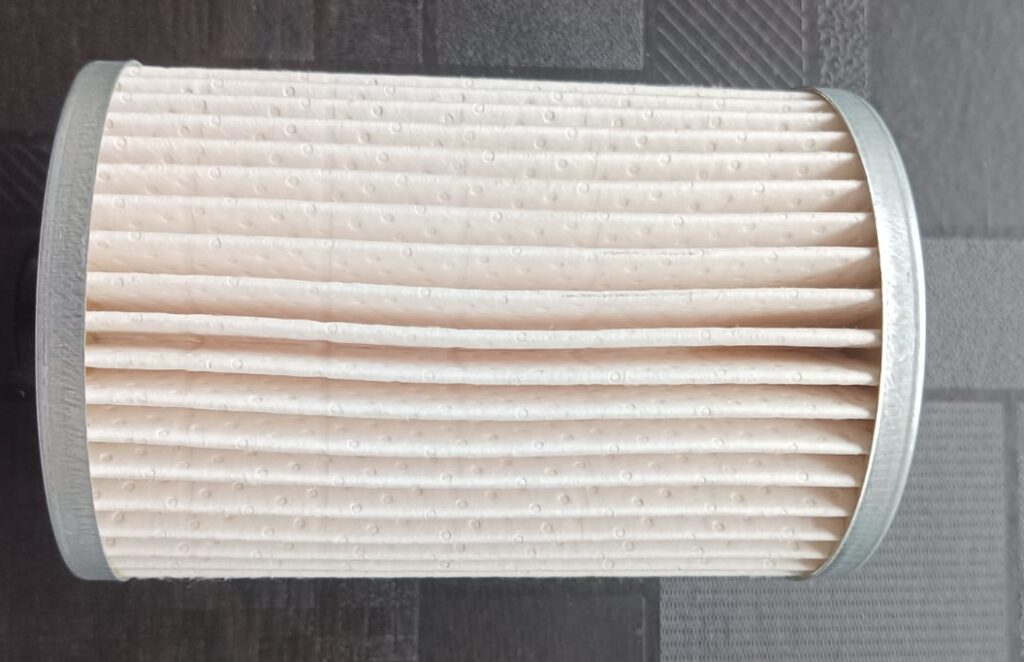
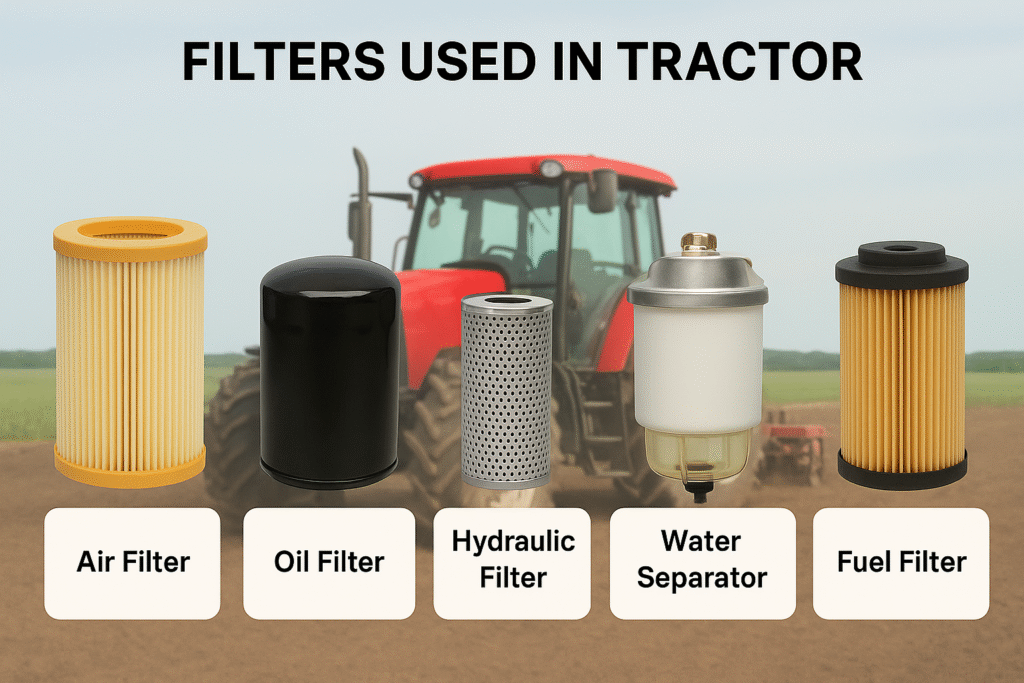
- Selection of service kit. Choosing the right service kit for your vehicle is a crucial step, as it contains essential parts like the oil filter, diesel filter, and air filter. Opting for high-quality, branded parts will ensure better performance. A good quality diesel filter will effectively filter the fuel for a longer period and maintain a consistent fuel supply to the engine. Similarly, if the oil filter is from a reputable brand, the oil will flow properly through the engine. Otherwise, a clogged oil filter can restrict the oil supply to various parts of the engine block. The air filter prevents dust and dirt from entering the engine. Choose your engine service kit carefully. Ideally, you should purchase it from an authorized service center. Alternatively, choose brands like Bosch Filters, Purolator Filters, Mann-Filters, K&N Filters, AC Delco Filters, or other trusted manufacturers.
- Fuel supply inspection. Ensure that the fuel supply line is in perfect condition. When you take your tractor for servicing, the service kit usually includes a diesel filter. The mechanic will typically only replace the diesel filter, but there can be other reasons for blockages in the fuel supply line. Firstly, there’s a filter in the fuel tank itself, which mechanics often don’t check. This filter can also accumulate dirt. Secondly, this dirt can also build up in the pipes; it can accumulate in all types of pipes. Then, there’s another filter located below the hand primer (fuel pump), which can also get clogged with dirt. There are also several other lines involved. Therefore, make sure all your fuel lines are clean.
- Inspect the radiator and water supply line. Checking the radiator and water supply is also very important. If the tractor driver is not careful and there is a leak in the radiator or water supply line, a water shortage can occur. This lack of water can cause problems in your engine, such as damaged pistons or rings, or even cause the engine to seize completely. This happens because water keeps the engine cool. If there is a problem with your radiator or water supply, there won’t be enough water in the radiator. If sufficient water doesn’t reach the engine, the engine can overheat and break down.
- Check the air intake capacity and its lines. Proper airflow in the engine is also crucial because speed is directly related to adequate airflow. Sometimes the filters are replaced, but other problems persist, such as damaged hose pipes or blockages in the filter after the air filter, which, if clogged, require manual cleaning. Start the engine and thoroughly inspect the hose pipes to ensure they are providing proper airflow, are free of leaks, are not damaged, and do not need replacing. Perform all these checks.
- Clutch and Break adjustment. / Comprehensive health checkup. Also, don’t forget to adjust the clutch and brakes. The adjustments can loosen over time. If the clutch and brakes are properly adjusted, they will function correctly for a longer period. Similarly, check all the bolts and nuts and tighten any that are loose. Check the lights and wiring, and then your tractor will be ready to operate.






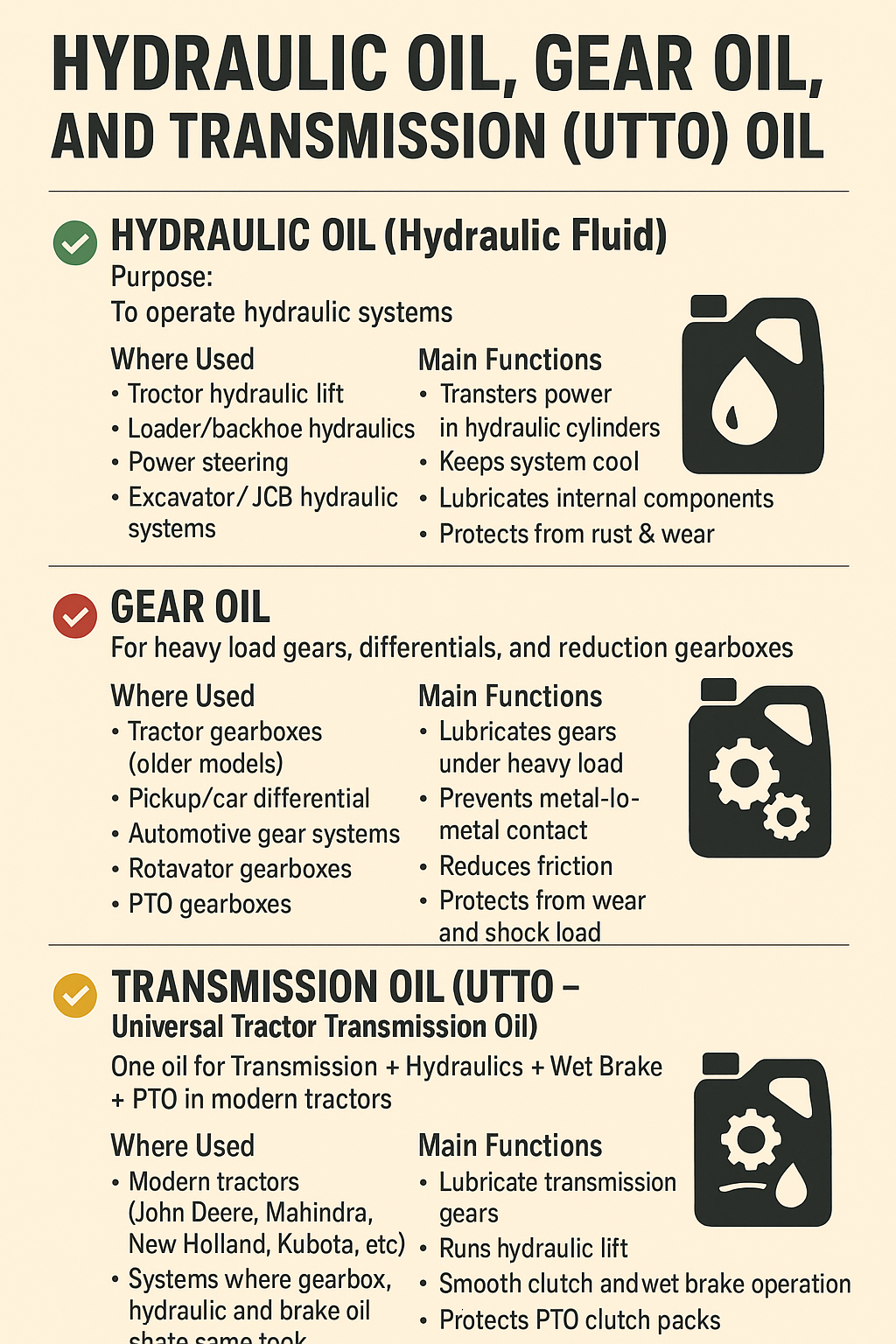







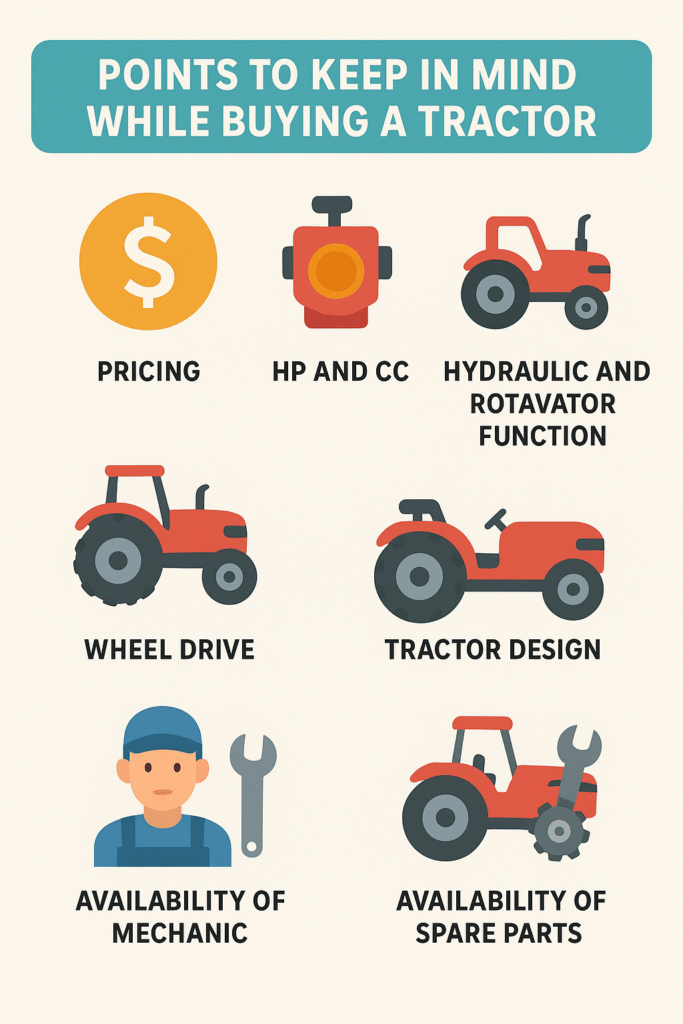
 factors to consider when selecting a tractor
factors to consider when selecting a tractor What kind of tractor works best in different farm situations
What kind of tractor works best in different farm situations What is commonly selected by farmers, in India
What is commonly selected by farmers, in India Points to consider (given that you’re in Bihar / probably engaged in small-, to medium-sized agriculture)
Points to consider (given that you’re in Bihar / probably engaged in small-, to medium-sized agriculture)