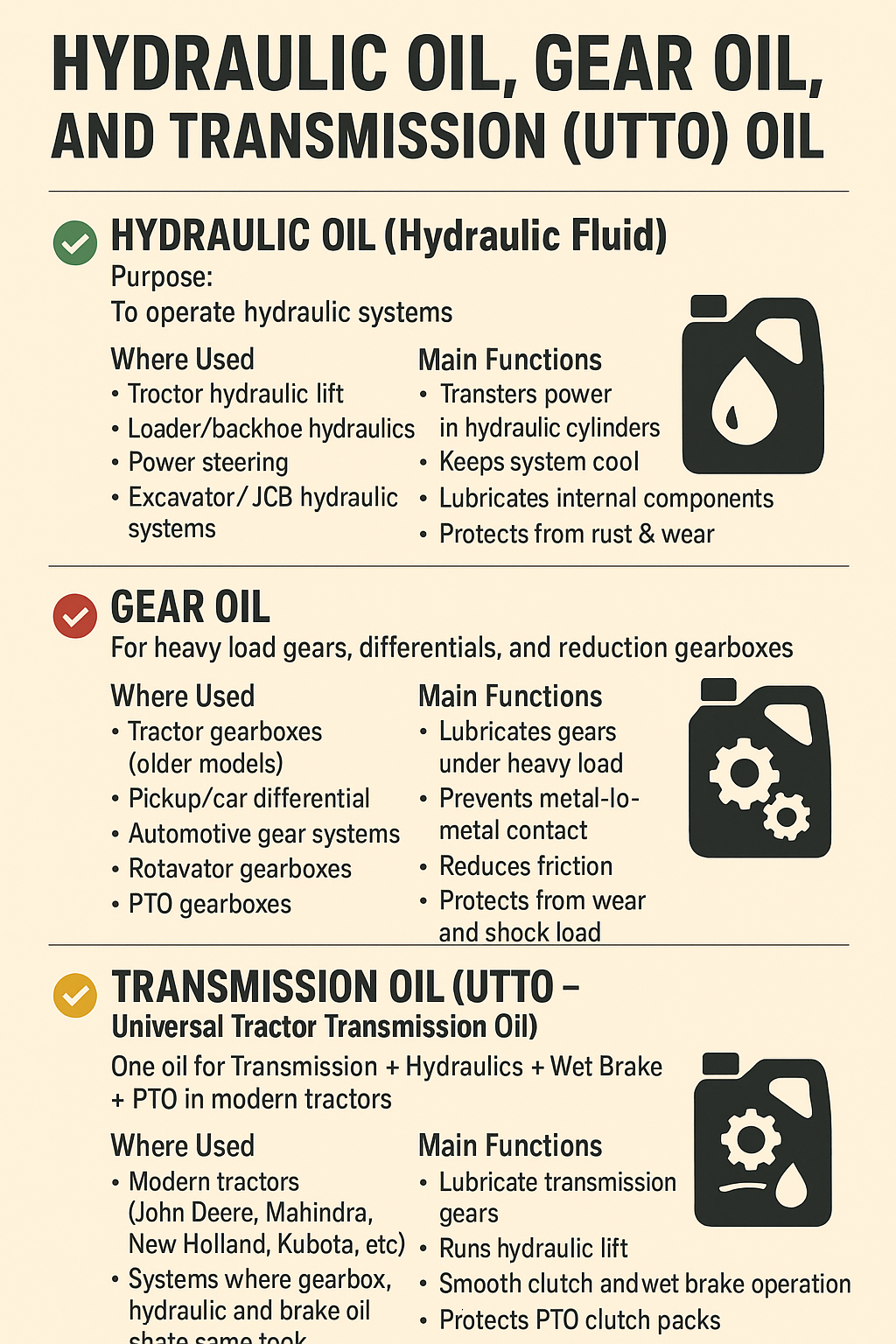
Difference between hydraulic gear and transmission oil.
♣ Difference Between Transmission Oil, Hydraulic Oil & Gear Oil.
Modern vehicles and machinery depend on several essential fluids that transfer power, reduce friction, and protect components. Three of the most important fluids are Transmission Fluid, Hydraulic Fluid, and Gear Oil. Although they may seem similar, each is designed for a specific purpose and works in different systems.
This article explains their roles, types, key differences, and applications.
◊ What is Transmission Oil (UTTO)?
Transmission fluid is a specially formulated lubricant used in automatic transmissions and some modern manual gearboxes.
It performs multiple tasks:
Lubricates gears and bearings
Reduces friction for smooth gear shifts
Provides hydraulic pressure inside automatic transmissions
Cools internal components
Ensures proper engagement of clutch packs and brake bands
Types of Transmission Fluid
Manual Transmission Oil (MTF)
Used in older cars; can thicken in winter, making shifting harder.Automatic Transmission Fluid (ATF)
Controls valves, lubricates internal parts, and supports torque converter performance.CVT Fluid
Designed only for Continuously Variable Transmissions. Using the wrong fluid can cause severe damage.
Benefits of Using Correct Transmission Oil
Smooth and reliable gear shifting
Reduced wear on gears and bearings
Lower friction and overheating
Better fuel efficiency and reduced emissions
◊ What is Hydraulic Oil ?
Hydraulic fluid is used in machines that operate using hydraulic pressure. The fluid transfers power, lubricates, cools components, and prevents rust.
Types of Hydraulic Oil.
Petroleum-Based Oils
Good lubrication and rust protection.Water-Based Fluids
Fire-resistant; available as emulsions or water-glycol blends.Synthetic Hydraulic Oils
Perform well at high temperatures; not suitable for all seals.Common hydraulic Oil Types
HM 32 – HM 46 – HM 68
◊ What is Gear Oil?
Gear oil is a high-viscosity lubricant used in gearboxes, differentials, and heavy-load gear systems.
Its primary purpose is to protect gears under high pressure and shock loads.
Functions of Gear Oil
Lubricates highly loaded gear teeth
Prevents metal-to-metal contact
Reduces heat in gear systems
Offers extreme pressure (EP) protection
Extends gearbox and differential life
Common Gear Oil Types
EP 80W-90, EP 85W-140
GL-4 / GL-5 specifications for automotive gear systems
Used in tractors, trucks, differentials, PTO gearboxes, and rotavators
◊ Transmission Oil vs Hydraulic Oil vs Gear Oil (Key Differences)
| Feature | Transmission Fluid | Hydraulic Fluid | Gear Oil |
|---|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Vehicle transmissions | Hydraulic systems | Gearboxes & differentials |
| Additives | Friction modifiers, anti-wear | Anti-foam, anti-rust | Extreme Pressure (EP), anti-scuff |
| Viscosity | Medium; stable for shifts | Medium to thick depending on system | Thick, high load capacity |
| Pressure Handling | Moderate | Very high | Very high gear pressure & shock load |
| Common Applications | Cars, tractors, loaders | Excavators, cranes, forklifts | Gearboxes, PTOs, axles |
◊ Applications
Transmission Oil
Passenger cars & SUVs
Trucks and buses
Modern tractors
Construction machinery with automatic transmissions
Hydraulic Fluid
Excavators, cranes, loaders
Forklifts and industrial machines
Aircraft landing systems
Hydraulic brakes
Gear Oil
Tractor and automotive gearboxes
Differentials and final drives
PTO gearboxes
Rotavator and tiller gear systems
◊ Conclusion
All three fluids—transmission Oil, hydraulic Oil, and gear oil—play a vital role in power transmission, but they are not interchangeable.
Hydraulic oil is used in hydraulic systems that require high pressure and smooth movement.
Transmission Oil. is designed specially for vehicle transmissions to ensure smooth shifting and lubrication.
Gear oil is formulated for high-load gear systems where strong EP protection is needed.
Selecting the correct oil based on manufacturer guidelines ensures better performance, longer equipment life, and lower maintenance costs.

